“Heating failed” in 3D printers can be a frustrating and time-consuming problem for operators to troubleshoot and resolve. The hot end and heat bed are two key components that rely on proper heating in order for the printer to function correctly. The failure of either of these components can cause a variety of issues, such as poor print quality, failed prints, or even damage to the printer itself.
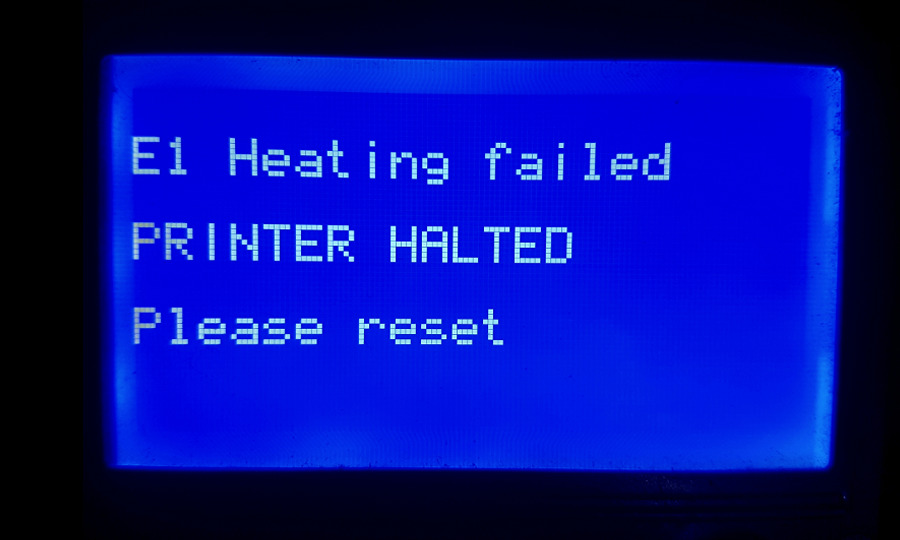
Hot end
Poor cables connection/Bad electrical conductivity
Connection of The Heating Cable
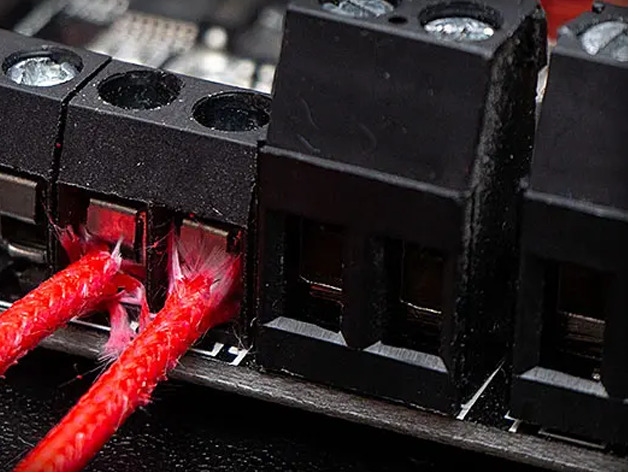
When experiencing heating failure in a 3D printer, one of the first things to check is the connection of the heating cable. The heating cable is responsible for providing power to the hot end or heat bed, so it is crucial that it is properly connected in order for the component to heat up correctly.
To ensure that the heating cable is well plugged into the board, you should first visually inspect the connection. Make sure that the cable is fully inserted into the appropriate port on the control board and that it is not loose or hanging out. If the cable appears to be properly connected, you should then check for proper electrical conductivity. This can be done with a multimeter by measuring the resistance of the cable. If the resistance is within the normal range, then the cable is likely in good working condition.
Additionally, it is important to properly fix the heating cable under the screws. This will ensure that the cable remains securely connected to the board and does not come loose during the printing process. Depending on the design of your printer, this may involve securing the cable with screws or clips. Make sure that all screws or clips are tightened properly, and that the cable is not pinched or damaged in the process.
In summary, to make sure the heating cable is well plugged into the board and properly fixed under the screws, you should visually inspect the cable’s connection, check for proper electrical conductivity, and ensure that the cable is securely fixed in place by screws or clips.
Connection of The Ceramic Heater
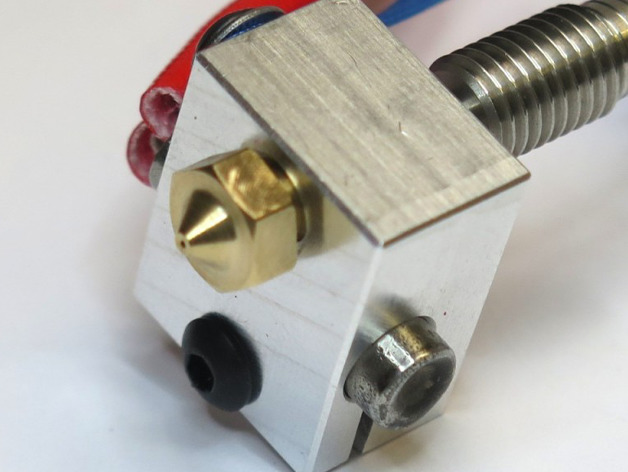
Another important step in troubleshooting heating failure in a 3D printer is to check the connection of the ceramic heater, which is the other end of the heating cable. The ceramic heater is a component that resides inside the heating block and is responsible for converting the electrical energy from the heating cable into heat. Therefore, it is essential that the ceramic heater is well inserted and installed in the heating block for the hot end or heat bed to function correctly.
To ensure that the ceramic heater is well inserted and installed in the heating block, you should first visually inspect the connection. Make sure that the ceramic heater is fully inserted into the heating block and that it is not loose or hanging out. If the ceramic heater appears to be properly inserted, you should then check for proper electrical conductivity. This can be done by measuring the resistance of the ceramic heater using a multimeter. If the resistance is within the normal range, then the ceramic heater is likely in good working condition.
Additionally, it is important to check the installation of the ceramic heater. Make sure that the ceramic heater is properly aligned and positioned within the heating block, and that it is not touching any other components or causing any interference. Also, check that the ceramic heater is fixed well in the heating block, ensuring that it is not loose and not moving.
Ensure the proper function of the thermistor, you should check that the thermistor cable is properly connected to the control board, and that the thermistor is not damaged and is properly fitted in the heating block. This will ensure that the control board receives accurate temperature information and can properly control the heating of the hot end or heat bed.
Layer cooling fan speed
During the 3D printing process, the layer cooling fan is used to cool down the layers of the printed object. However, if the speed of the fan is too high or it is running at full capacity, it can cause sudden cooling of the hot end and result in a temperature drop that is faster than the control board’s ability to heat. This can lead to heating failure and poor print quality.
To prevent this problem, it is recommended to turn on the cooling fan gradually, starting at a low percentage, such as 20%, and then gradually increasing until it reaches its normal speed. This will allow the hot end to adjust to the cooling and prevent sudden drops in temperature.
Additionally, installing a silicone cover on the hot end can also help to stabilize the temperature and partially insulate it. This can prevent heat loss and help the control board to maintain a consistent temperature, which in turn will improve the print quality and prevent heating failure.
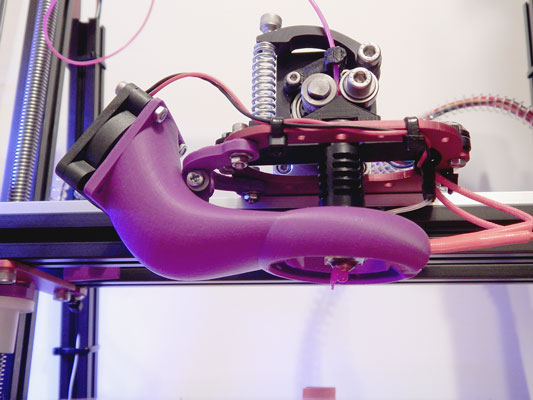
Heat Bed
Ensure the proper function of the heating cable for the heat bed, you should check that the heating cable is securely connected to its port on the control board or external MOSFET and that the cable is properly installed and not pinched or damaged. This will ensure that the heat bed receives the necessary power to heat up correctly and maintain a stable temperature.
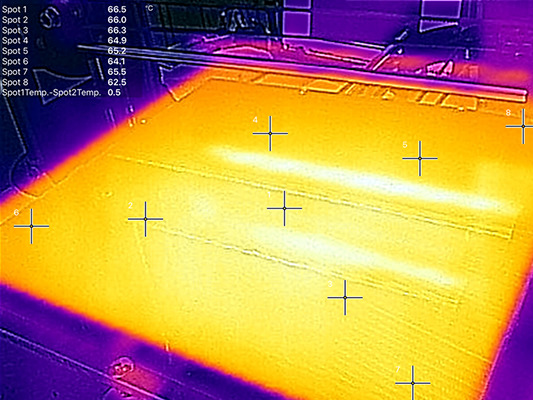
Check that the heating cables are still soldered well into the heat bed. This will ensure that the heat bed receives the necessary power to heat up correctly and maintain a stable temperature.
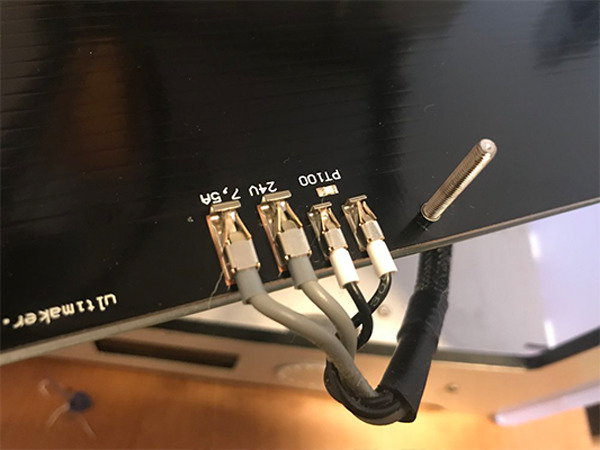

It is important to check that the thermistor cable is properly connected to its port on the control board and that the thermistor is well connected to the heat bed. This will ensure that the control board receives accurate temperature information and can properly control the heating of the heat bed.

The heat bed in a 3D printer has a relatively large heating area, which results in a higher heat transfer rate. This means that the heat bed dissipates more heat than other components in the printer. When the temperature around the printer is low, it can make it difficult for the heat bed to reach and maintain the desired temperature, which can lead to a heating failure.
To avoid this problem, it is important to keep the temperature around the printer within a normal range. This can be achieved by ensuring that the room temperature is not too low. Additionally, using an insulated cover around the printer can help to retain the heat, making it easier for the heat bed to reach the desired temperature and maintain it.
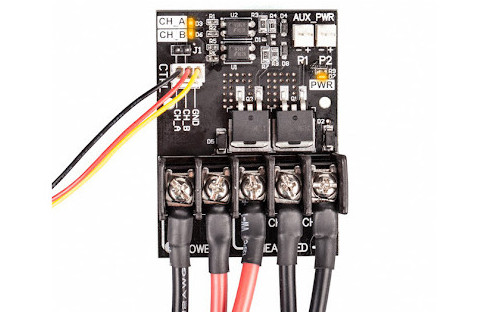
High-power MOSFETs are highly recommended for use with heat beds in 3D printers because they provide the heat bed with a large amount of power, making it easy to heat up the bed and keep its temperature stable.