What is nylon material?
Nylon is a thermoplastic synthetic polymer known for its high strength and durability. It is created by polymerizing an amide monomer and was first developed by DuPont in 1935. It has a wide range of applications such as mechanical parts, gears, textiles, automotive industry, electrical components, household appliances, and plastic products. Nylon fibers are also used to make fishing line, ropes, and other items that require strength and resistance to abrasion. It is a versatile material that is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties.

Why is nylon filament used in 3d printing?
Nylon filament is a popular choice for 3D printing due to its unique properties and characteristics. One of the main advantages of nylon filament is its low coefficient of friction, which makes it an ideal material for printing moving parts such as gears and mechanical components. This low coefficient of friction results in parts that move smoothly and with less wear and tear, making them more durable and long-lasting.
In addition, nylon filament has excellent impact resistance, meaning that it can withstand high impacts and forces without breaking or deforming. This makes it ideal for printing parts that will be exposed to high stress or impact, such as protective covers and other mechanical components.
Nylon filament also has excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and durability. This makes it ideal for printing parts that will be exposed to heavy loads or high stress, such as gears and other mechanical components. Additionally, Nylon is a wear-resistant material which means it will last longer and maintain its properties even when exposed to friction or abrasion.
Heat resistance is another property of nylon filament, it can withstand high temperatures and maintain its properties, which makes it suitable for printing designs that require high-temperature resistance.
However, nylon filament also has some drawbacks, such as high moisture absorption. This means that it can absorb moisture from the air, which can affect its printing properties and weaken layer-to-layer adhesion. This can result in poor print quality and warping of the final printed part. Nylon filament also has a high warping susceptibility, which can make it more difficult to print with, especially when printing large or complex parts.
Before starting 3d printing
keep nylon filament dry
Nylon filament is known for its high moisture absorption, which can negatively impact print quality and weaken layer-to-layer adhesion. To ensure that your nylon filament is dry and ready for printing, it is important to store it in a dry place. One way to do this is by using an airtight container with a moisture-absorbent material. This will help to keep the filament dry and protect it from absorbing moisture from the air.
Additionally, if you are printing a model that takes a long time, it is recommended to use a filament dryer. A filament dryer is a device that can dry out the filament by heating it up to a certain temperature, which removes the moisture and makes the filament ready for printing. This is especially useful if you are planning on printing a model that takes a long time, as it will ensure that the filament remains dry throughout the entire printing process.

Hot end
When printing with Nylon filament, it is important to use a hotend that can withstand the high temperatures required to print with this material. Nylon filament is typically printed at temperatures of 250°C or higher, which means that it is not suitable for use with PTFE-lined hotends. PTFE, also known as Teflon, is a type of plastic that is commonly used in hotends but it cannot withstand temperatures above 250°C, which is why it is not suitable for printing with Nylon filament.
Instead, it is recommended to use an all-metal hotend for printing with Nylon filament. All-metal hotends are made from materials that can withstand high temperatures, such as steel, brass or aluminum. This means that they will not degrade or melt at the high temperatures required for printing with Nylon filament, and will provide a stable and consistent heat source for your print. By using an all-metal hotend, you can ensure that your Nylon filament is printed correctly and that the final print quality is good.
Use enclosure
When printing with Nylon filament, one of the main challenges is dealing with shrinkage and warping. This occurs because Nylon filament is printed at high temperatures, and as it solidifies, the temperature drops rapidly. This rapid cooling can cause the filament to shrink and warp, which can negatively impact the final print quality.
To combat this problem, it is recommended to use an enclosure around the 3D printer. The enclosure will help to maintain a stable and consistent temperature around the model as it is being printed. This will prevent the model parts from experiencing significant temperature differences, which in turn reduces the shrinkage and warping that can occur. The enclosure will keep the air temperature around the model relatively high and stable, which will help to prevent warping.
It is recommended to keep the ambient temperature of the enclosure between 40-80°C, this will ensure the nylon filament will be able to maintain its properties and avoid warping.

Apply a strong adhesive
By using a strong adhesive, you can ensure that the printed part stays in place as it cools and solidifies, preventing any warping from occurring. This is a simple yet effective way to improve print quality and make sure your print comes out as expected.
Print settings
Printing temperature
When printing with Nylon filament, it is essential to use the correct printing temperature. Most Nylon filaments are typically printed at temperatures between 240-260°C. However, it is important to note that different manufacturers may have different recommended printing temperatures for their Nylon filaments.
Before starting to print with a new Nylon filament, it is recommended to perform some test prints to determine the ideal temperature for that specific filament.
Heat bed temperature
The optimal heat bed temperature for printing with Nylon filament is typically between 65-100°C. This temperature range allows the filament to maintain good adhesion to the build plate while preventing it from overheating and warping. It is important to keep in mind that the ideal heat bed temperature can vary depending on the specific filament and print conditions. It is recommended to check the manufacturer’s recommended heat bed temperature range and to perform some test prints to determine the ideal temperature.
Brim
A brim is a single-layer flat area that is added around the base of a 3D model during the slicing process. It is designed to keep the edges of the print down and increase the contact area between the model base and the build plate. This is particularly useful when printing with materials that are prone to warping, such as Nylon filament, as it helps to keep the bottom surface of the print flat and fully adhered to the build plate.
When using slicing software such as Ultimaker Cura, the width of the brim can be adjusted to meet the specific needs of the print. A wider brim will provide a larger adhesion area which will reduce the likelihood of warping. It is recommended to use a brim width of 12 mm or greater when printing with Nylon filament to ensure that the adhesion area is sufficient and to minimize warping. This can be adjusted as needed to fine-tune the print results.
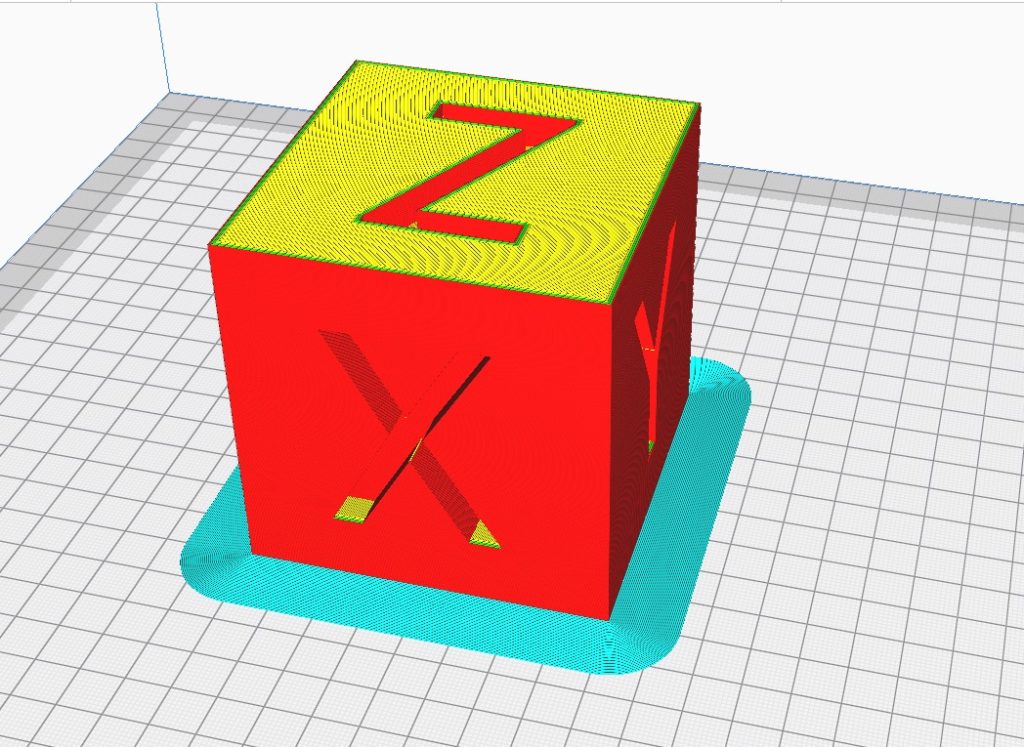
Raft
A raft is a thick base layer that is added to a 3D model during the slicing process. It is typically used when printing models with small contacting areas between the model and the build plate. The purpose of the raft is to improve the adhesion of the model to the build plate, by providing a larger surface area for adhesion.
A raft is similar to a brim in that it increases the contact area between the part and the build plate, and thus increases the adhesion of the part to the build plate. However, while a brim is a single layer flat area around the base of the model, a raft is a thick plate that sits between the model and the build area.
In some designs, such as gears, a brim may not be preferred because it is difficult to remove due to the narrow space at the teeth area. In such cases, a raft is preferred as it is easier to remove and does not interfere with the narrow spaces.
When using slicing software, the raft settings can be adjusted to meet the specific needs of the print. The extra margin, or the distance between the raft and the model, and the number of top layers, or the thickness of the raft, can be adjusted.
Raft extra margin: 20 mm
Raft top layers: 4
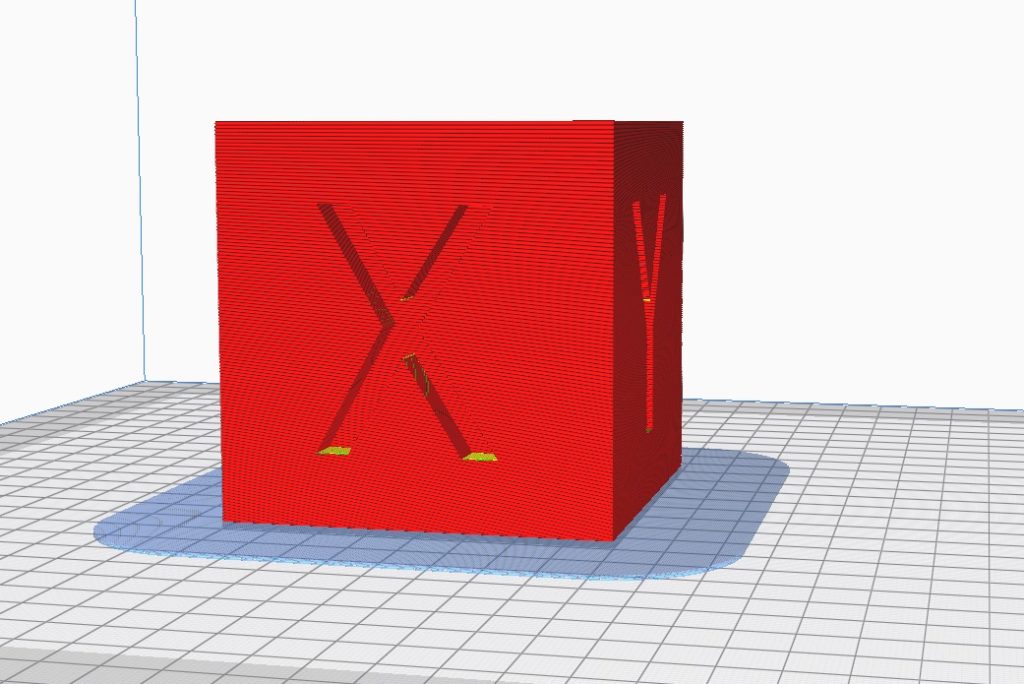
Cooling fan
To avoid shrinkage and poor adhesion issues caused by a high-speed cooling fan, it is recommended to set the cooling fan speed to 0 for the first 4 layers of the print. Gradually increasing the fan speed to a range of (0-40)% will ensure proper cooling while minimizing the risk of warping and poor adhesion.

Print speed
Recommended print speed for nylon filament is (20-40) mm/s.
note: All the settings mentioned in this article are based on the Cura slicer. The printing settings are only general guidelines for printing with nylon filament successfully. It is recommended that you do your own testing. To adapt these settings to the specific needs of each design.